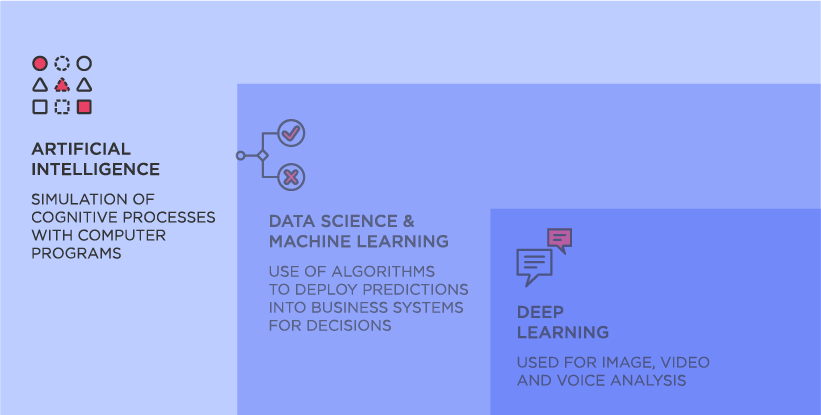
What is artificial intelligence?
Artificial intelligence (AI) encompasses a wide range of technologies (such as NLPs, LLMs, GenAI, ML, and more) capable of performing dedicated tasks normally associated with human cognition. These include problem-solving, understanding language, and interpreting sensory input such as images, video, or sound.
Types of artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a broad field of advanced technologies, spanning many tools and solutions. From speech recognition, to computer vision, text generation, chatbots, and even self-driving cars, AI encompasses many of our daily, digital lives. There are many disciplines and subsets within AI:
Machine Learning
Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of AI that involves advanced data analysis performed without explicit programming instructions. ML algorithms can “learn” by consuming information from multiple sources, identifying patterns, and making recommendations.
Deep learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that involves many layers of neural networks. Neural networks are a specific type of ML model inspired by the structure and functioning of the human brain. They consist of interconnected layers of artificial "neurons" (also called “nodes”) that process data to recognize patterns and make predictions or decisions.
There are several types of neural networks such as:
- Artificial neural network (ANN)
- Convolutional neural networks (CNNs)
- Recurrent neural networks (RNNs)
Natural Language Processing
Natural Language Processing (NLP), another subset of AI, enables machines to understand, interpret, and respond to human language. This technology can ingest textual information like articles, academic papers, and written reports, eliciting meaning and discerning contextual nuances. NLP has provided a foundation for generative AI (GenAI) through the advancement of large language models (LLMs).
Large language models
Large Language Models (LLMs) are a subset and key advancement of NLP, made up of deep learning models designed to generate human language at scale. These models are trained on massive datasets, with data points in the billions. LLM models are first pre-trained on large datasets and then fine-tuned by data scientists for more specific tasks relevant to their use case.
Well-known GenAI tools like ChatGPT, BERT, Gemini, and Llama are all LLMs.
Generative AI and Agentic AI
GenAI is a newer technology capable of creating original content such as text, images, and music. Although GenAI is the most widely known subset of the larger field of artificial intelligence, it is a relatively recent development that only comprises part of the picture.
Recent innovations have skyrocketed the usage of GenAI, leading to exploration into agentic AI. Generative AI has gained incredible popularity since the launch of ChatGPT in 2022. Since then, people around the world have incorporated AI into their daily lives and workflows.
Agentic AI is the next level of AI, no longer requiring human prompts, but operating in dynamic environments to make decisions autonomously (like self-driving vehicles). Agentic AI focuses on actions and decision making, while GenAI is focused on the creation of text, images, videos, and other types of content, usually based on inputs from a human prompt.
There are many other branches and subfields of AI not covered here, as this technology is rapidly advancing into every area of modern society.
Applications of AI in business
AI has already proven it can lead to cost reduction, more efficiency, and intelligent decision making—making it top of mind for key business leaders who want to gain a competitive edge. Businesses are aggressively deploying AI to address a wide range of use cases:
Predictive maintenance
Predictive analytics, for example, helps manufacturers keep production lines operating smoothly by collecting machine data, identifying patterns that indicate potential failures, and recommending preemptive maintenance that helps prevent unplanned downtime.
Anomaly detection
Anomaly detection looks for statistical outliers, which can reveal potential problems that might not otherwise be apparent. Banks use anomaly detection to identify suspicious credit card transactions, also known as fraud detection. Law enforcement agencies use it to spot unusual behavior that might merit closer investigation.
Cost, asset, and resource optimization
This technology can also be deployed for cost optimization and asset optimization. Using AI-driven anomaly detection in Spotfire, you can visualize where spending is happening and gain a better view of areas where your organization may be overspending or underspending.
Benefits of implementing AI
Although AI may have gained popular attention for its ability to compose term papers and create original artwork, numerous applications in the business world deliver meaningful real-world benefits. These benefits include operational efficiency, improved data-driven decisions, reduced waste, and better customer experiences.
Improve decision making with hidden insights
The Scottish Environment Protection Agency (SEPA) uses Spotfire machine learning capabilities to identify never-before-seen patterns in its data. That data provides the basis for sound decisions about the agency’s future programs aimed at solving persistent challenges that are often hidden from plain sight. By arming its field personnel with mobile devices running Spotfire visual analytics, SEPA improves both the speed and quality of its decisions.
Increase operational efficiency and safety
Since 2020, the Italian government has relied on Autostrade per l’Italia to manage roads and highways throughout the country—using real-time insights to keep traffic flowing smoothly, prevent accidents, and optimize construction and maintenance efforts. With Spotfire's help, Autostrade per l’Italia holistically manages data from traffic patterns, construction activity, auto accidents, weather events, and other incidents. By leveraging AI-embedded Spotfire technology, the company’s frontline experts have immediate access to advanced intelligence that helps them keep Italy’s roads safer.
Potential challenges and concerns with AI
Numerous observers have noted concerns about AI's impact on society. While many of those scenarios call to mind science fiction movies that stoke fears about renegade AI technology, there are nevertheless very real concerns that business leaders should consider in the present:
Environmental concerns
AI technologies tend to consume very large amounts of energy, for example. Data centers use more electrical power every year as they scale up to handle increasing technology burdens. Water is also at risk, as it’s needed to cool off these systems, using copious amounts of a scarce resource. In the rush to roll out artificial intelligence, we should weigh the benefits against its environmental costs, much of which haven’t been fully studied or anticipated.
Our two previous examples (Autostrade per l’Italia and the Scottish Environment Protection Agency) underscore AI's clear benefits. AI-powered analytics help SEPA with its core mission of protecting the environment. For Autostrade per l’Italia, the efficient traffic flow means less idle time, which translates to lower CO2 emissions. When AI helps lower environmental impact, it can help offset the costs of deploying AI, and this offset should always be a clear goal in companies that plan to adopt this technology throughout their enterprise.
Social and ethical considerations
Researchers and governmental agencies alike have noted many ethical concerns and social considerations with this new technology. As legislation struggles to keep up with the advancements in AI, many business leaders are hesitant to readily adopt advanced models in their IT infrastructure without further consideration.
AI models can be biased and heighten implicit biases already in data sets, especially demographic biases. This is a major concern when AI is used in industries that impact people’s personal lives, like healthcare, financing, and law enforcement.
There’s also the concern of copyright infringement and intellectual property with GenAI technology. Because LLMs require massive data sets to train each model, many developers are using information found on the internet to do so. However, not all of the internet is accurate or even free to use, leading models to generate content that uses proprietary data or misleading information. Whose data is being used to train these models? How does GDPR come into play? Can models be truly comprehensive and unbiased without using personal data? Leaders are still grappling with these concerns, and legislation is slow to answer.
Finally, many advanced AI models are unexplainable, meaning their creators can’t pinpoint how or why the model came to a specific decision. This is a concern for businesses and legislators alike. If the model can’t be explained, then unintended biases remain hidden in the “black box” logic of the tool.
Difficult to implement
Other challenges include the difficulty some companies have experienced in deploying AI technologies. Emerging technologies are often characterized by early-stage project failures, especially when organizations try to build custom solutions from scratch. A far better approach is to work with established platforms aimed at delivering a core set of capabilities for specific industries and use cases. Organizations can get the best of both worlds by selecting a proven platform and extending its capabilities to suit their unique business needs, reducing project risk without sacrificing bespoke functionality.
AI deploys real value
It’s clear that AI-driven solutions aren’t going anywhere, despite the many challenges organizations may face to utilize this cutting-edge technology.
Spotfire offers immediate value by delivering industry-specific solutions for financial services, energy, manufacturing, life sciences, telecommunications, and more. It also empowers teams to customize and develop custom analytics applications effortlessly using low-code tools with powerful data science capabilities that increase speed-to-insight. With embedded AI, Spotfire offers predictive analytics and large language models (LLMs) that make it faster and easier to generate game-changing insights.
Want to learn more? Explore AI-driven Spotfire capabilities for deeper data-driven insights.
Related resources
Learn about how Spotfire combines industry-specific visualizations with cutting-edge solutions to solve your most complex problems.
Turn predictive findings into optimal outcomes with the latest advancements in AI and ML.
